Cluster alternatives and similar libraries
Based on the "Maps" category.
Alternatively, view Cluster alternatives based on common mentions on social networks and blogs.
-
Mapbox GL
DISCONTINUED. Interactive, thoroughly customizable maps in native Android, iOS, macOS, Node.js, and Qt applications, powered by vector tiles and OpenGL -
NAMapKit
Allows you to use custom maps in iphone applications and attempts to mimics some of the behaviour of the MapKit framework -
CMMapLauncher
CMMapLauncher is a mini-library for iOS that makes it quick and easy to show directions in various mapping applications. -
JDSwiftHeatMap
JDSwiftMap is an IOS Native MapKit Library. You can easily make a highly customized HeatMap. -
MapViewPlus
DISCONTINUED. Use any custom view as custom callout view of your MKMapView with cool animations. Also, easily use any image as annotation view. -
GoogleMapsHelper
An easy to integrate Model Based Google Maps Helper (SVHTTPClient, AFNetworking) That lets you Geo Code , Reverse Geocode, Get Directions , Places Autocomplete. -
GLMap
Crossplatform offline vector map with MapCSS styling. Offline search and offline navigation are included.
WorkOS - The modern identity platform for B2B SaaS

* Code Quality Rankings and insights are calculated and provided by Lumnify.
They vary from L1 to L5 with "L5" being the highest.
Do you think we are missing an alternative of Cluster or a related project?
README

Cluster is an easy map annotation clustering library. This repository uses an efficient method (QuadTree) to aggregate pins into a cluster.
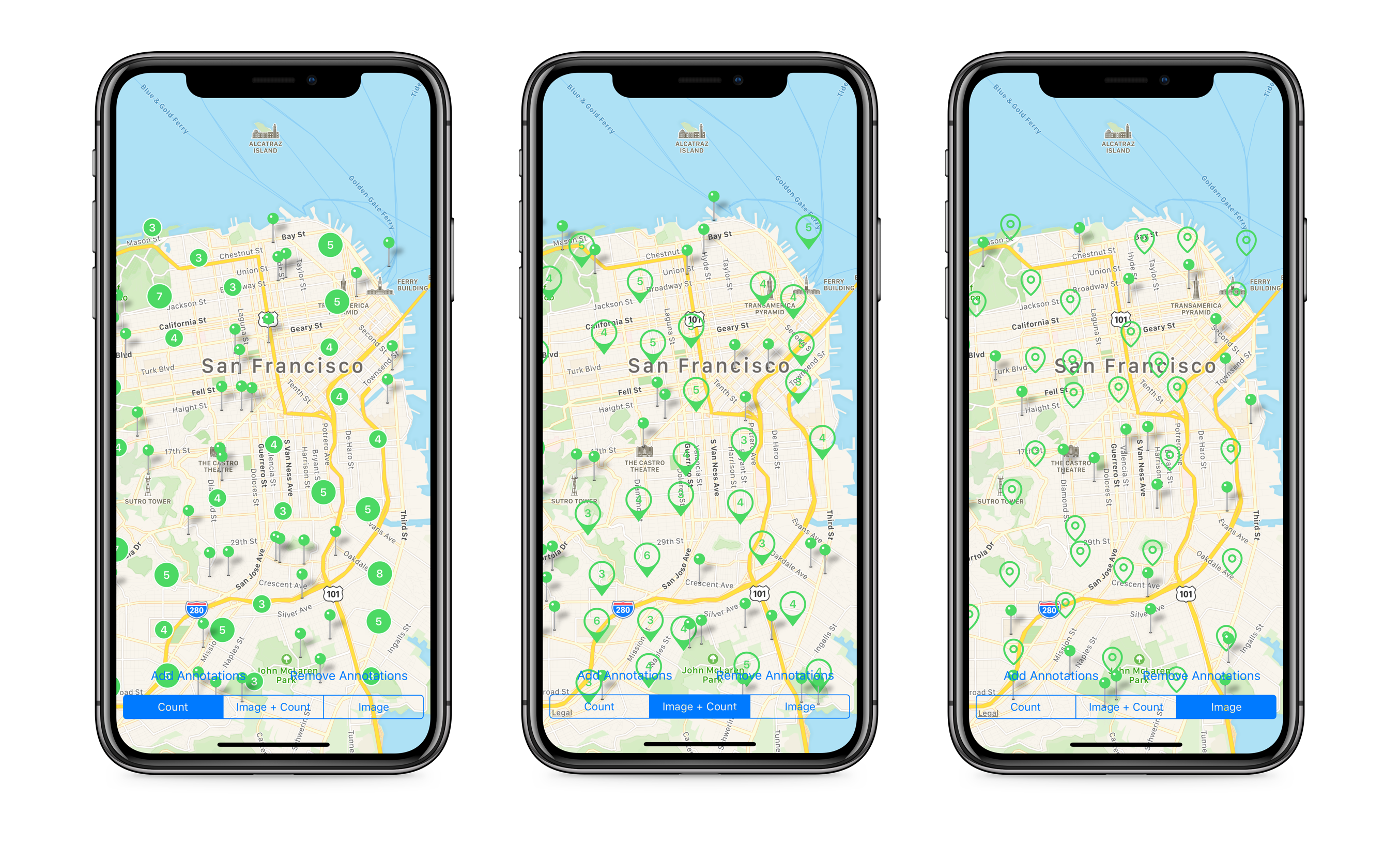
Features
- [x] Adding/Removing Annotations
- [x] Clustering Annotations
- [x] Multiple Managers
- [x] Dynamic Cluster Disabling
- [x] Custom Cell Size
- [x] Custom Annotation Views
- [x] Animation Support
- [x] Documentation
Requirements
- iOS 8.0+
- Xcode 9.0+
- Swift 5 (Cluster 3.x), Swift 4 (Cluster 2.x), Swift 3 (Cluster 1.x)
Demo
The [Example](Example) is a great place to get started. It demonstrates how to:
- integrate the library
- add/remove annotations
- reload annotations
- configure the annotation view
- configure the manager

$ pod try Cluster
Installation
Cluster is available via CocoaPods and Carthage.
CocoaPods
To install Cluster with CocoaPods, add this to your Podfile:
pod "Cluster"
Carthage
To install Cluster with Carthage, add this to your Cartfile:
github "efremidze/Cluster"
Usage
The Basics
The ClusterManager class generates, manages and displays annotation clusters.
let clusterManager = ClusterManager()
Adding an Annotation
Create an object that conforms to the MKAnnotation protocol, or extend an existing one. Next, add the annotation object to an instance of ClusterManager with add(annotation:).
let annotation = Annotation(coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 21.283921, longitude: -157.831661))
manager.add(annotation)
Configuring the Annotation View
Implement the map view’s mapView(_:viewFor:) delegate method to configure the annotation view. Return an instance of MKAnnotationView to display as a visual representation of the annotations.
To display clusters, return an instance of ClusterAnnotationView.
extension ViewController: MKMapViewDelegate {
func mapView(_ mapView: MKMapView, viewFor annotation: MKAnnotation) -> MKAnnotationView? {
if let annotation = annotation as? ClusterAnnotation {
return CountClusterAnnotationView(annotation: annotation, reuseIdentifier: "cluster")
} else {
return MKPinAnnotationView(annotation: annotation, reuseIdentifier: "pin")
}
}
}
For performance reasons, you should generally reuse MKAnnotationView objects in your map views. See the [Example](Example) to learn more.
Customizing the Appearance
The ClusterAnnotationView class exposes a countLabel property. You can subclass ClusterAnnotationView to provide custom behavior as needed. Here's an example of subclassing the ClusterAnnotationView and customizing the layer borderColor.
class CountClusterAnnotationView: ClusterAnnotationView {
override func configure() {
super.configure()
self.layer.cornerRadius = self.frame.width / 2
self.layer.masksToBounds = true
self.layer.borderColor = UIColor.white.cgColor
self.layer.borderWidth = 1.5
}
}
See the [AnnotationView](Example/AnnotationView.swift) to learn more.
Annotation Styling
You can customize the appearance of the StyledClusterAnnotationView by setting the style property of the annotation.
let annotation = Annotation(coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 21.283921, longitude: -157.831661))
annotation.style = .color(color, radius: 25)
manager.add(annotation)
Several styles are available in the ClusterAnnotationStyle enum:
color(UIColor, radius: CGFloat)- Displays the annotations as a circle.image(UIImage?)- Displays the annotation as an image.
Once you have added the annotation, you need to return an instance of the StyledClusterAnnotationView to display the styled annotation.
func mapView(_ mapView: MKMapView, viewFor annotation: MKAnnotation) -> MKAnnotationView? {
if let annotation = annotation as? ClusterAnnotation {
return StyledClusterAnnotationView(annotation: annotation, reuseIdentifier: identifier, style: style)
}
}
Removing Annotations
To remove annotations, you can call remove(annotation:). However the annotations will still display until you call reload().
manager.remove(annotation)
In the case that shouldRemoveInvisibleAnnotations is set to false, annotations that have been removed may still appear on map until calling reload() on visible region.
Reloading Annotations
Implement the map view’s mapView(_:regionDidChangeAnimated:) delegate method to reload the ClusterManager when the region changes.
func mapView(_ mapView: MKMapView, regionDidChangeAnimated animated: Bool) {
clusterManager.reload(mapView: mapView) { finished in
// handle completion
}
}
You should call reload() anytime you add or remove annotations.
Configuring the Manager
The ClusterManager class exposes several properties to configure clustering:
var zoomLevel: Double // The current zoom level of the visible map region.
var maxZoomLevel: Double // The maximum zoom level before disabling clustering.
var minCountForClustering: Int // The minimum number of annotations for a cluster. The default is `2`.
var shouldRemoveInvisibleAnnotations: Bool // Whether to remove invisible annotations. The default is `true`.
var shouldDistributeAnnotationsOnSameCoordinate: Bool // Whether to arrange annotations in a circle if they have the same coordinate. The default is `true`.
var distanceFromContestedLocation: Double // The distance in meters from contested location when the annotations have the same coordinate. The default is `3`.
var clusterPosition: ClusterPosition // The position of the cluster annotation. The default is `.nearCenter`.
ClusterManagerDelegate
The ClusterManagerDelegate protocol provides a number of functions to manage clustering and configure cells.
// The size of each cell on the grid at a given zoom level.
func cellSize(for zoomLevel: Double) -> Double? { ... }
// Whether to cluster the given annotation.
func shouldClusterAnnotation(_ annotation: MKAnnotation) -> Bool { ... }
Communication
- If you found a bug, open an issue.
- If you have a feature request, open an issue.
- If you want to contribute, submit a pull request.
Mentions
Credits
- https://github.com/ribl/FBAnnotationClusteringSwift
- https://github.com/choefele/CCHMapClusterController
- https://github.com/googlemaps/google-maps-ios-utils
- https://github.com/hulab/ClusterKit
License
Cluster is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.
*Note that all licence references and agreements mentioned in the Cluster README section above
are relevant to that project's source code only.






